中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 650-656.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1444
• 生物材料循证医学 evidence-based medicine of biomaterials • 上一篇
囊袋技术与经皮穿刺椎体后凸成形治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折:评价改善伤椎术后cobb角及减少骨水泥渗漏的Meta分析
李凯明1,王尚全2,李玲慧2,朱立国1,张 清1,谢 瑞1
- 中国中医科学院望京医院,1脊柱二科,2骨伤综合科,北京市 100102
Bone filling bag vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fractures: a meta-analysis of improving Cobb angle and reducing bone cement leakage
Li Kaiming1, Wang Shangquan2, Li Linghui2, Zhu Liguo1, Zhang Qing1, Xie Rui1
- 1Second Department of Spine Surgery, 2Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Traditional Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China
摘要:

文题释义:
囊袋技术:是通过向椎体内置入囊袋,借助压力注射系统向高分子网层状结构的囊袋内灌注骨水泥,扩张囊袋,使椎体高度恢复。继续灌注的骨水泥透过网格渗出,渗入到骨折裂隙,形成微观绞锁,达到加固病椎、减少骨水泥渗漏的目的。
经皮穿刺椎体后凸成形术:该技术采用椎体内置入气囊扩张的方法使椎体复位,在椎体内部形成空隙,减小骨水泥注入所需的推力,使骨水泥在椎体内不易流动。可有效解除或缓解疼痛,恢复病椎的高度,但临床发现仍存在骨水泥渗漏等风险。
背景:目前对于囊袋技术与经皮穿刺椎体后凸成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折的临床疗效是否存在差异尚有争论。
目的:通过系统评价比较囊袋技术与经皮穿刺椎体后凸成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折的有效性及安全性。
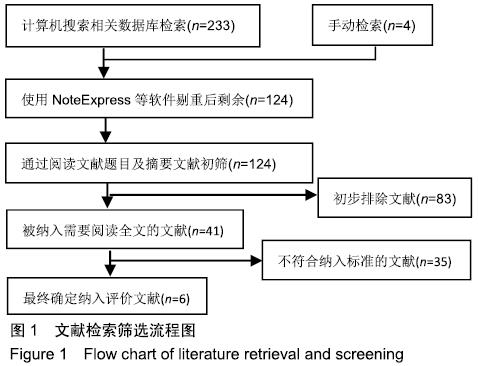
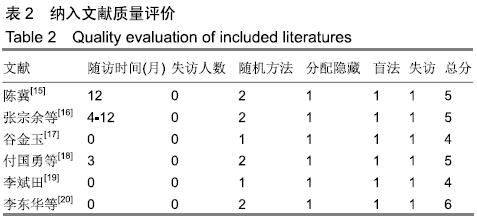
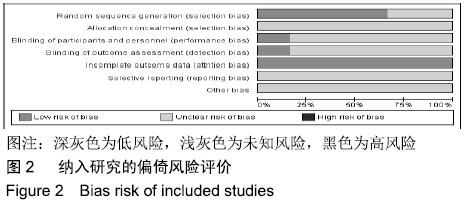
方法:计算机检索在2019年2月之前公开发表在中国知网(CNKI)、万方、维普、CBM、EMBASE、MEDLINE及Cochrane图书馆数据库中的所有关于囊袋技术与经皮穿刺椎体后凸成形术治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折的随机对照研究和国内外临床试验。由2位研究员独立进行文献筛选、数据提取,按Cochrane协作网标准对纳入随机对照试验逐个进行质量评价,对符合纳入标准的研究用RevMan 5.3软件进行Meta分析。
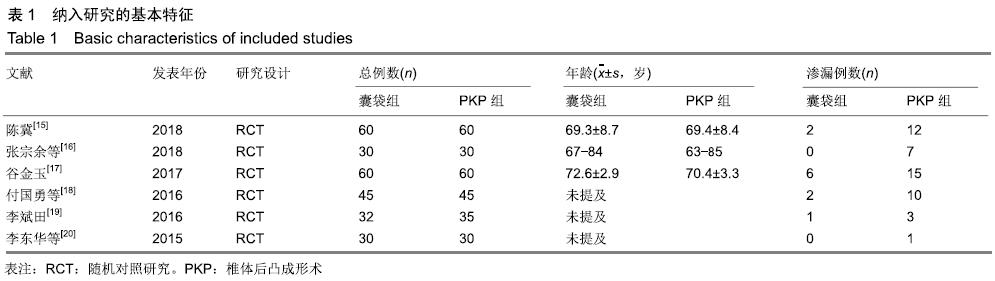
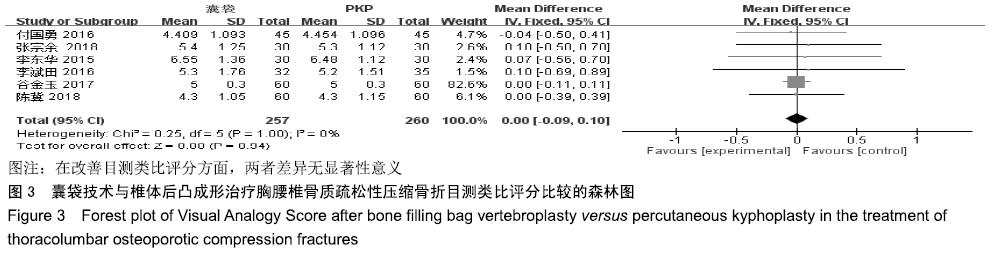
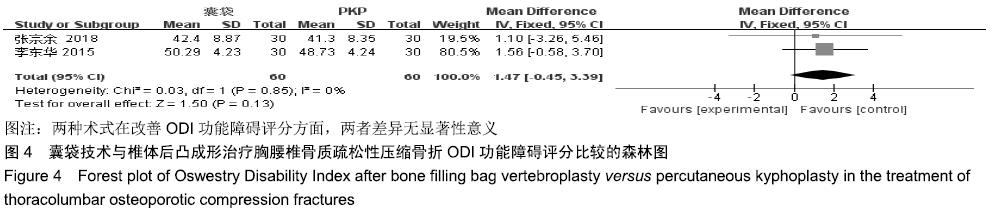
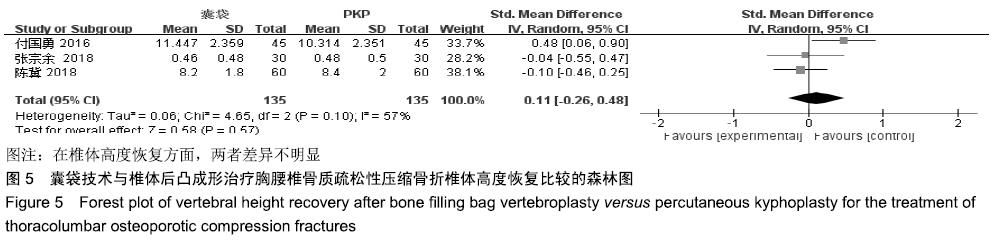
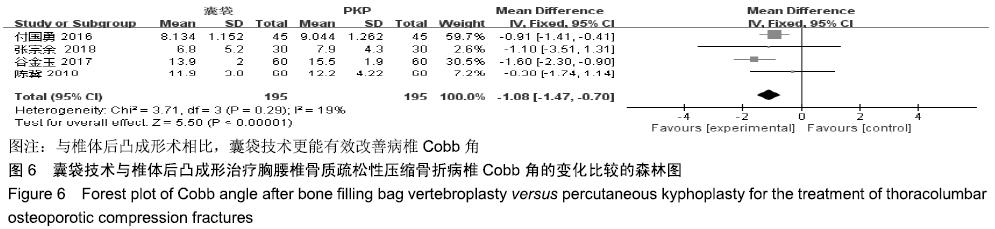
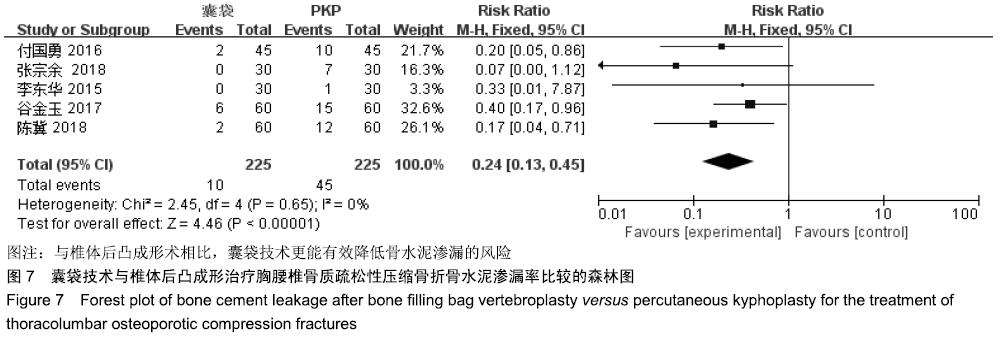
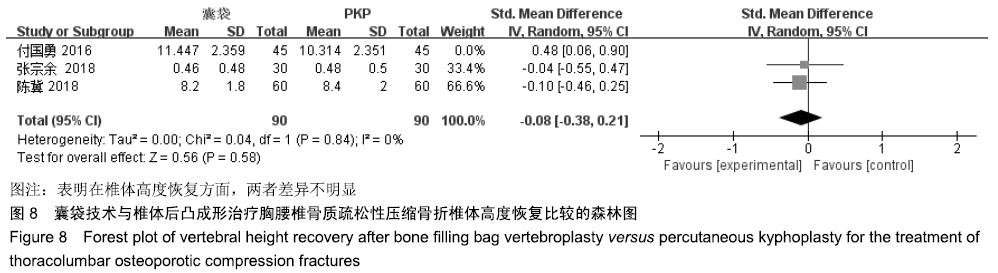
结果与结论:①最终纳入6篇随机对照试验,共517例患者,其中囊袋技术组257例,经皮穿刺椎体后凸成形术组260例;②Meta分析结果显示:两种术式在改善胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折患者目测类比评分(MD=0.00,95%CI:-0.09-0.10,P=0.94)、椎体高度恢复(SMD=0.11,95%CI:-0.26-0.48,P=0.57)、治疗后ODI功能障碍评分(MD=1.47,95%CI:-0.45-3.39,P=0.13)等方面差异均无显著性意义,但在术后cobb角(MD=-1.08,95%CI:-1.47至-0.70,P < 0.000 01)、骨水泥渗漏率(RR=0.24,95%CI:0.13-0.45,P < 0.000 01)方面均有显著性意义;③上述结果证实,与经皮穿刺椎体后凸成形术相比,囊袋技术在改善伤椎术后cobb角及减少骨水泥渗漏等并发症发生率方面具有显著优势,在目测类比评分、椎体高度恢复、ODI功能障碍评分等临床疗效相似,因此后期仍需大量高质量的多中心随机对照研究提供更充足的证据。ORCID: 0000-0001-8871-3539(李凯明)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: